
| 一般情况 | |
|---|---|
 | 品种:混种猫 |
| 年龄:2个月 | |
| 性别:雌 | |
| 是否绝育:否 | |
| 诊断:畸胎瘤 | |
01 主诉及病史
消瘦,难以吞咽固体食物。
02 检查
口腔内检查发现,在右侧硬腭-软腭过渡区有一个肿块(下图)。肿块向喙侧生长,气道未阻塞,仅表现出吞咽困难。
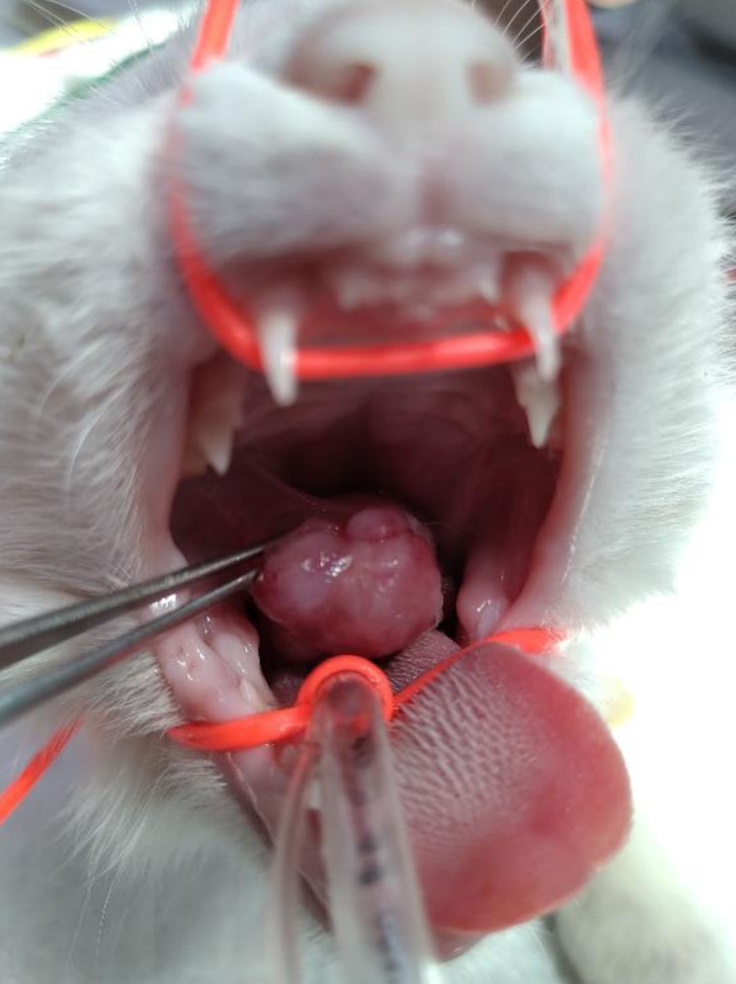
03 治疗
手术切除了肿块,并进行了病理检查。
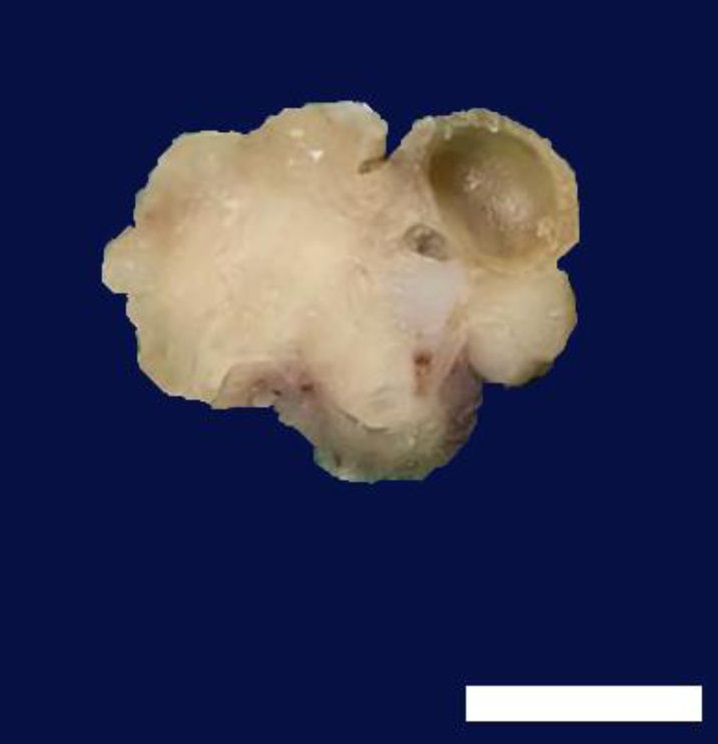
病理显示,肿瘤边缘清晰,呈圆形,表面不规则,直径约2 cm。切面由白色至灰色的实性组织组成,囊肿长达7 mm(下图)。
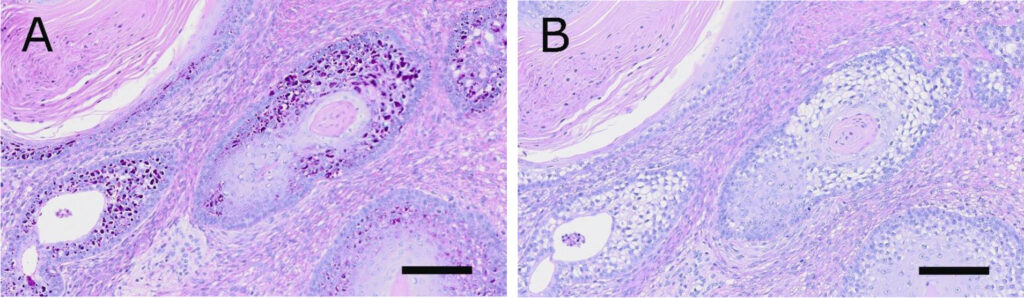
肿块主要由未成熟的间质细胞组成,囊肿内可见非角化和部分角化的分层鳞状上皮、纤毛上皮、腺上皮或细胞质空泡上皮,以及少量分化的毛囊、凋亡腺和皮脂腺(下图)。大多数含有空泡的上皮细胞位于基底层和角质层之间。

空泡细胞含有大量细胞质糖原,而基底层和角质层几乎没有糖原(下图)。一些上皮巢的基底层细胞出现外周苍白化。存在未成熟和成熟的软骨岛,成熟的软骨岛表现出软骨内骨化,骨小梁腔不含骨髓,但有成骨细胞附着在骨小梁上。
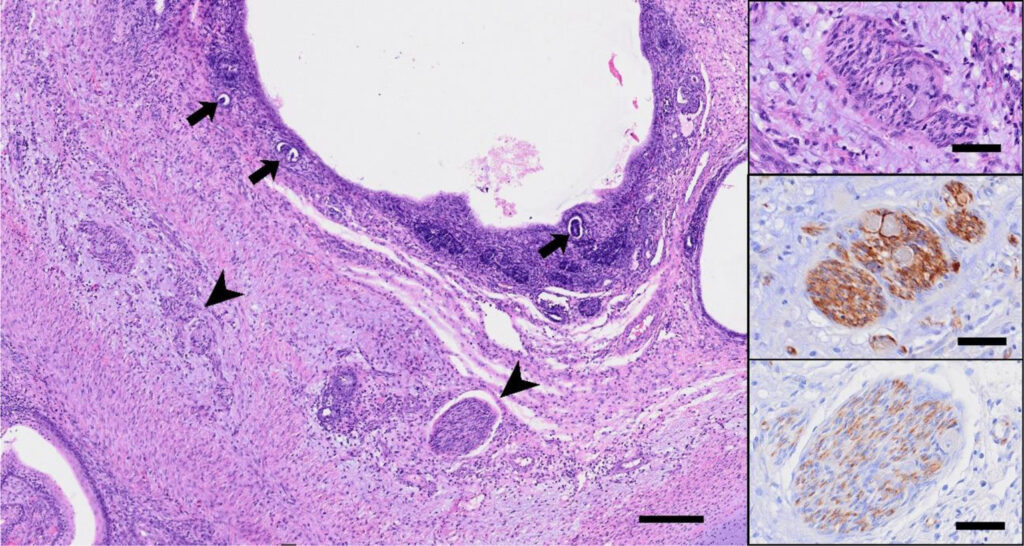
还观察到未成熟的神经上皮形成神经上皮花环的病灶,周围有神经胶质组织(下图)。
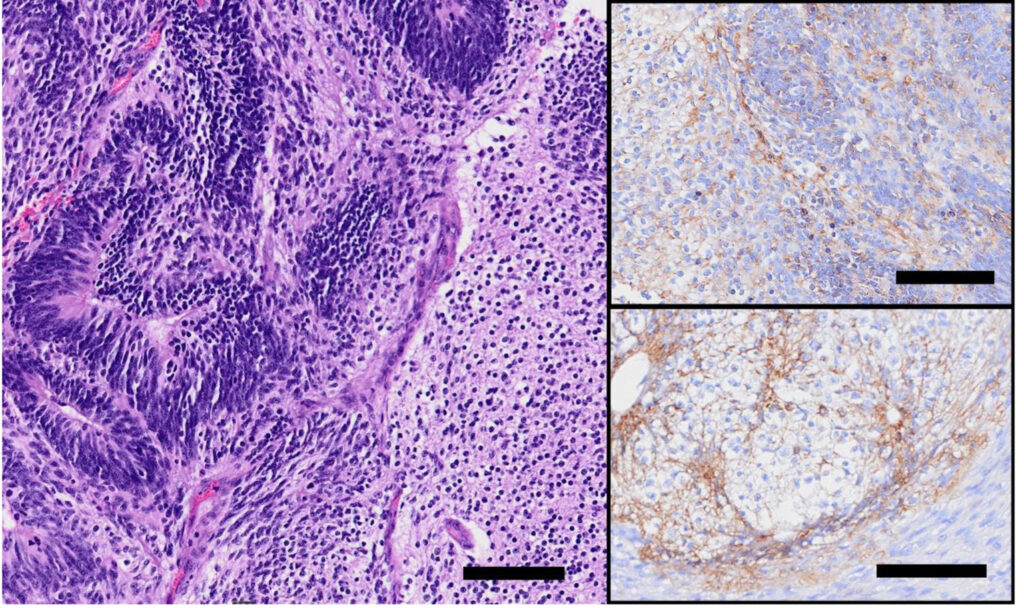
肾母细胞结构位于带有小腺泡细胞的单纯上皮周围,一些神经节散布在肾母细胞成分周围(下图)。
小的蓝色细胞构成未成熟的肾小管或肾小球结构(下图)。
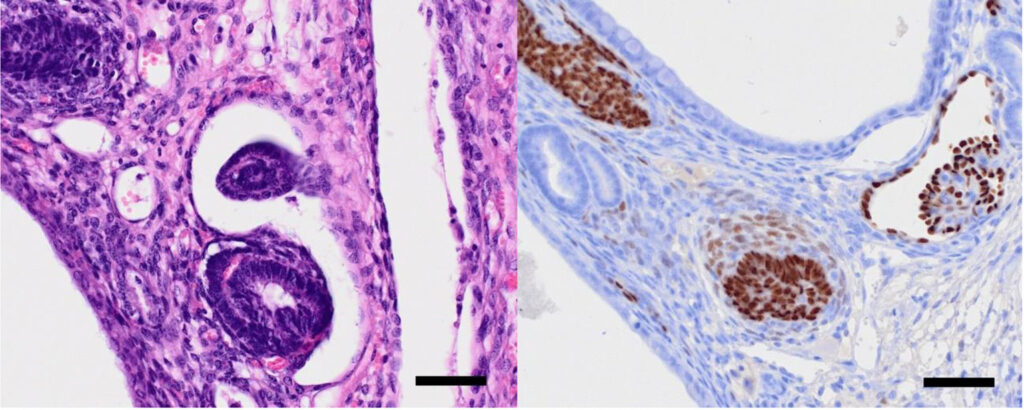
免疫组化染色结果:神经上皮细胞nestin和波形蛋白呈阳性,增殖指数较高(Ki67:62.9%)。基质、软骨和神经基质组织的波形蛋白和S100阳性,神经基质显示GFAP阳性。所有上皮细胞类型的AE1/AE3均为阳性。所有肾母细胞成分WT1和波形蛋白均呈核阳性。胚泡细胞和上皮细胞的AE1/AE3也呈阳性。这些组织学和免疫组化结果符合含有肾母细胞成分的未成熟畸胎瘤。
04 预后
切除术后一个月,肿块所在的口腔粘膜被正常粘膜覆盖,没有复发迹象。体格检查没有发现颅面畸形。
05 讨论
畸胎瘤是源自多能干细胞的先天性肿瘤,含有异源成分。它们被定义为由两个或三个生殖层中可识别的元素组成的肿瘤[1]。畸胎瘤通常出现在性腺,也可发生在性腺外组织。
既往报道了6只猫的睾丸外畸胎瘤,包括颅内、头部、眼球后、尾骨、尾部和会阴[4,6,11,16,23,25],其中5只猫的年龄小于1岁。口咽部位的畸胎瘤在动物中仅有两例报道,除本病例外在猫中从未有过报道[7,8]。
人类畸胎瘤根据细胞分化情况分为成熟型和未成熟型。成熟畸胎瘤由上皮、软骨、骨和腺组织等分化良好的组织组成。未成熟畸胎瘤含有不同数量的未成熟组织,其中可能混有成熟成分。此外,未成熟畸胎瘤还包括原始神经外胚层组织[15,20]。在人类文献中,畸胎瘤中出现肾母细胞成分的情况极为罕见[9,26]。
口咽畸胎瘤在人和兽医学中都极为罕见[2,7,8,14,27]。人类口咽畸胎瘤的发病率约占新生儿的1/35000到1/200000。头颈部畸胎瘤占所有畸胎瘤的2-9%[2]。人类口咽畸胎瘤的死亡率很高,可导致呼吸困难或吞咽困难[17,27]。此外,人类口咽畸胎瘤患者可能会同时出现颅面畸形。腭裂是最常见的畸形[12,17]。
仅有两例关于牛和羚羊口咽畸胎瘤的报道[7,8]。一例羚羊病例因气道阻塞而在产后早期死亡[7],一例牛病例患有颊颌畸形和口瘘[8]。在猫的病例报告中,咽部皮样囊肿[13]并未报告单纯口咽畸胎瘤。本例畸胎瘤表现为吞咽困难,但无气道阻塞,也未伴有颅面畸形。
未成熟畸胎瘤通常含有神经上皮、软骨和原始间充质组织。肿瘤中是否存在未成熟的神经外胚层对诊断未成熟畸胎瘤非常重要,也是与成熟畸胎瘤的一个鉴别点[15,20]。根据Norris人卵巢畸胎瘤三级分级系统,肿瘤分级基于未成熟神经外胚层灶的总量和不典型性[15,20]。如果按此分级,本畸胎瘤属于低级别。
不过,儿童的神经外胚层并不会降低其预后。儿童期未成熟畸胎瘤只有在伴有恶性生殖细胞(通常是卵黄囊肿瘤)和临床恶性肿瘤(如转移瘤)的情况下才会被认为是恶性的[2,20,22]。在人类医学中,新生儿畸胎瘤(包括口咽未成熟畸胎瘤)手术切除后的存活者预后良好[18,21]。在本病例中,虽然观察时间很短,但仅靠手术切除预后表现良好。
在这种肿瘤中,有大量富含糖原的上皮细胞。毛囊外根鞘的下峡部和上下部有大量糖原[24]。而在组织发生过程中,角质形成细胞显示出清晰的细胞质,并有大量糖原沉积[10,19]。因此,富含糖原的上皮可能代表组织发生期或外根鞘分化期的未成熟上皮。
此外,在该病例中,WT1阳性的肾母细胞成分是混合的。畸胎瘤合并肾母细胞瘤(TWN)在人类中非常罕见。大多数TWN发生在肾脏,但也发现一些肾脏以外的病例,包括口咽部病变[26]。TWN的定义是50%以上的肿块由畸胎成分和肾母细胞成分混合组成[5]。然而TWN的发病机制仍存在争议,如果肾母细胞区是肾脏外的次要成分,就像本病例一样,则可能是未成熟畸胎瘤中肾母细胞成分的胚胎起源[3,26]。这种情况更倾向于认为未成熟畸胎瘤具有肾母细胞成分,而不是TWN。
本病例是第一例猫口咽畸胎瘤,也是第一例家养物种中带有肾母细胞成分的畸胎瘤。尽管口咽畸胎瘤极为罕见,但仍应将其列入幼猫口腔肿块的鉴别诊断中。手术切除是避免因呼吸和喂养困难而导致产后早期死亡的主要治疗方法。
参考文献
1. Agnew DW, MacLachlan NJ. 2017. Tumors of the genital systems. p. 698. In: Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed. (Meuten DJ ed.), Willey Blackwell, Ames.
2. Carvalho CHP, Nonaka CFW, Elias CTV, Matheus RCS, Dias RMB, Souza LB, Pinto LP. 2017. Giant epignathus teratoma discovered at birth: a case report and 7-year follow-up. Braz Dent J 28: 256–261.
3. Cheng CH, Yang SH, Su B. 2016. Nephroblastic elements in a retroperitoneal immature teratoma with elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein. J Case Rep 2: 15–19.
4. Chénier S, Quesnel A, Girard C. 1998. Intracranial teratoma and dermoid cyst in a kitten. J Vet Diagn Invest 10: 381–384.
5. Fernandes ET, Parham DM, Ribeiro RC, Douglass EC, Kumar APM, Wilimas J. 1988. Teratoid Wilms’ tumor: the St Jude experience. J Pediatr Surg 23: 1131–1134.
6. Goethem B, Bosmans T, Chiers K. 2010. Surgical resection of a mature teratoma on the head of a young cat. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 46: 121–126.
7. Haefele HJ, Guthrie A, Trupkiewicz JG, Garner MM. 2008. Oropharyngeal teratoma in a neonatal sable antelope (Hippotragus niger). J Zoo Wildl Med 39: 266–269.
8. Ibrahim A, Mohamed AAS, Abdelbaset AE. 2022. Parrot mouth and oronasal fistula with a presumed teratoma hanging from the soft palate in a cattle calf. J Adv Vet Res 12: 318–320.
9. Ince EZ, Cekmez F, Yıldırım Ş, Demirel A, Bilgic B, Kılıcaslan I, Coban A. 2013. Malignant epignathus including a nephroblastoma component and successful management. Ann Diagn Pathol 17: 288–290.
10. Isales MC, Tan T, Maesden L. 2019. Skin. pp. 377–384. In: Color Atlas of Human Fetal and Neonatal Histology, 2nd ed. (Ernst LM, Ruchelli ED, Carreon CK, Huff, DS eds.), Springer, Cham.
11. Kegler K, Kröner B, Baumgärtner W, Wohlsein P. 2015. Feline coccygeal teratoma: Immunohistochemical characterization of mature and immature tissue components. J Comp Pathol 152: 65.
12. Kishi Y, Soh S, Tanaka S, Nitta A, Matsushima A. 2020. A case of congenital teratoma with cleft palate in a neonate. Arch Clin Med Case Rep 04: 746–753.
13. Koch L, Csebi P, Lipnik K, Gradner G. 2022. Pharyngeal dermoid cyst causing partial upper airway obstruction in a cat. JFMS Open Rep 8: 20551169221122853.
14. Narayan R, Ahmad MS, Sr, Kumar A. 2020. Fetal Oropharyngeal Teratoma: Prenatal Diagnosis and Imaging Characteristics. Cureus 12: e11329.
15. Norris HJ, Zirkin HJ, Benson WL. 1976. Immature (malignant) teratoma of the ovary: a clinical and pathologic study of 58 cases. Cancer 37: 2359–2372.
16. Ober CA, Taulescu M, Oana L, Bel L, Cătoi C, Fărcas L, Pestean C. 2013. An unusual case of a mature teratoma on the left perineal region of a young cat: surgical treatment and pathological description. Acta Vet Scand 55: 51.
17. Okhakhu AL, Onyeagwara NC. 2022. Oropharyngeal teratoma: A case presentation and review of literature. Afr J Paediatr Surg 19: 179–182.
18. Pellegrini V, Colasurdo F, Guerriero M. 2021. Epignathus with oropharynx destruction. Autops Case Rep 11: e2021293.
19. Serri F, Montagna W, Mescon H. 1962. Studies of the skin of the fetus and the child. II. Glycogen and amylophos-phorylase in the skin of the fetus. J Invest Dermatol 39: 199–217.
20. Shinkai T, Masumoto K, Chiba F, Shirane K, Tanaka Y, Aiyoshi T, Sasaki T, Ono K, Gotoh C, Urita Y, Takayasu H, Suzuki R, Sakashita S. 2020. Pediatric ovarian immature teratoma: Histological grading and clinical characteristics. J Pediatr Surg 55: 707–710.
21. Singh S. 2020. Mature teratoma in a neonate presenting as an intraoral cystic lesion: A case report. Indian J Child Health (Bhopal) 7: 274–276.
22. Too S, Ahmad Sarji S, Yik Y, Ramanujam T. 2008. Malignant epignathus teratoma. Biomed Imaging Interv J 4: e18.
23. Sirivisoot S, Siripara N, Arya N, Techangamsuwan S, Rungsipipat A, Kasantikul T. 2022. Case report: Mature extragonadal teratoma at the proximal part of the tail in a kitten. Front Vet Sci 9: 1003673.
24. Wiener DJ. 2021. Histologic features of hair follicle neoplasms and cysts in dogs and cats: a diagnostic guide. J Vet Diagn Invest 33: 479–497.
25. Wray JD, Doust RT, Fraser McConnell, Dennis RT, Blunden AS. 2008. Retrobulbar teratoma causing exophthalmos in a cat. J Feline Med Surg 10: 175–180.
26. Wu Y, Chu C, Zhang J, Nitish B, Ni J, Xu X. 2022. A case of ovarian Teratoma with nephroblastoma presenting abdomen metastasis. J Clin Lab Anal 36: e24364.
27. Zhu P, Li XY. 2021. Management of oropharyngeal teratoma: Two case reports and a literature review. J Int Med Res 49: 300060521996873.